The Next-Gen of Storage Virtualization for Modern Cloud Computing
Mar 13th, 2024 | 7 min read
What is Storage Virtualization?
Storage virtualization, as a concept, has been around for about 60 years now. However, it became more prominent and practical with the advancement of computing technologies in the late 1990s and early 2000s, particularly with the emergence of storage area networks (SANs) and network-attached storage (NAS). As these systems became more prevalent, storage virtualization technologies took advantage of these architectures, offering more scalable and flexible solutions for managing your storage resources.
Storage Virtualization Architectures
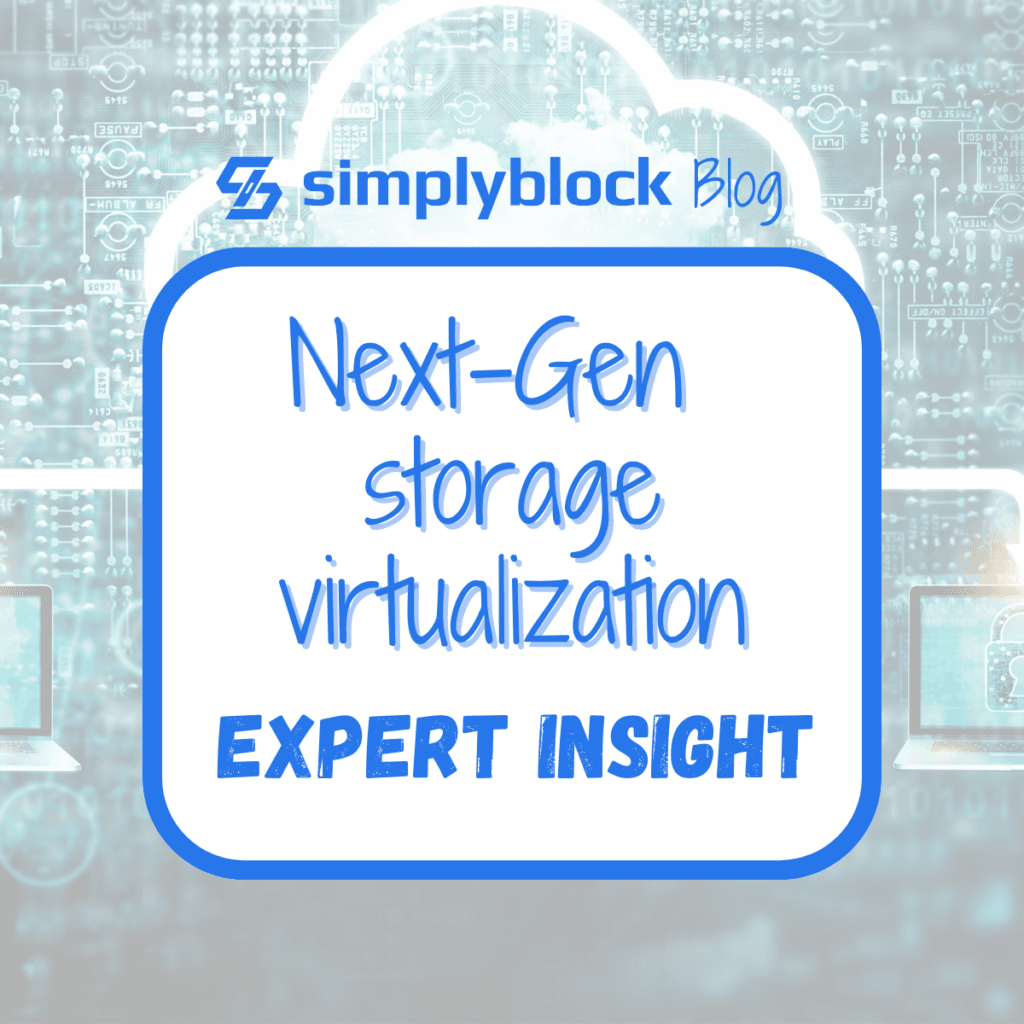
The idea of storage virtualization abstracts away the physical storage resources from the logical view presented to users or applications. This abstraction allows for more efficient management of storage resources in terms of time and resources. The separation enables the pooling of multiple physical storage devices into a single logical storage pool. Furthermore, different types of disks can be used to tier data from faster but more expensive storage backends to slower but cheaper ones, optimizing cost and performance. All complexities are hidden by providing the user with a logical (or virtual) device, providing the client with heterogeneous storage.
In addition to physical resource management, additional features help improve storage efficiency by utilizing deduplication and compression. This architecture provides features like thin provisioning, data migration, and replication without requiring direct interaction with the underlying hardware.
Storage virtualization architectures integrate solutions such as disk mirroring, checksums, transaction support, and other durability features to provide built-in high availability, redundancy, and fault tolerance. Therefore, those systems easily mitigate the loss of one or more backing storage devices and provide the necessary integrity for enterprise-level data storage.
Today, storage virtualization is a fundamental component of modern storage infrastructures. They include various technologies, such as software-defined storage (SDS), virtual storage appliances (VSAs), Kubernetes storage, or storage hypervisors. Accordingly, this enables organizations to achieve greater agility, scalability, and efficiency in managing their storage environments.
Storage in the Cloud Age
With the emergence of cloud environments and companies redesigning their existing services or building newer architectures, storage requirements have also shifted to the cloud, resulting in the loss of many beloved features.
When consuming storage-as-a-service, such as Amazon EBS, we can take advantage of some storage virtualization concepts. At the same time, we also have to live with limitations on the existing cloud storage services. For organizations looking to transition storage efficiently, Block Storage Migration provides a structured approach to moving workloads while ensuring flexibility and avoiding vendor lock-in.
The Choice of Storage in the Cloud
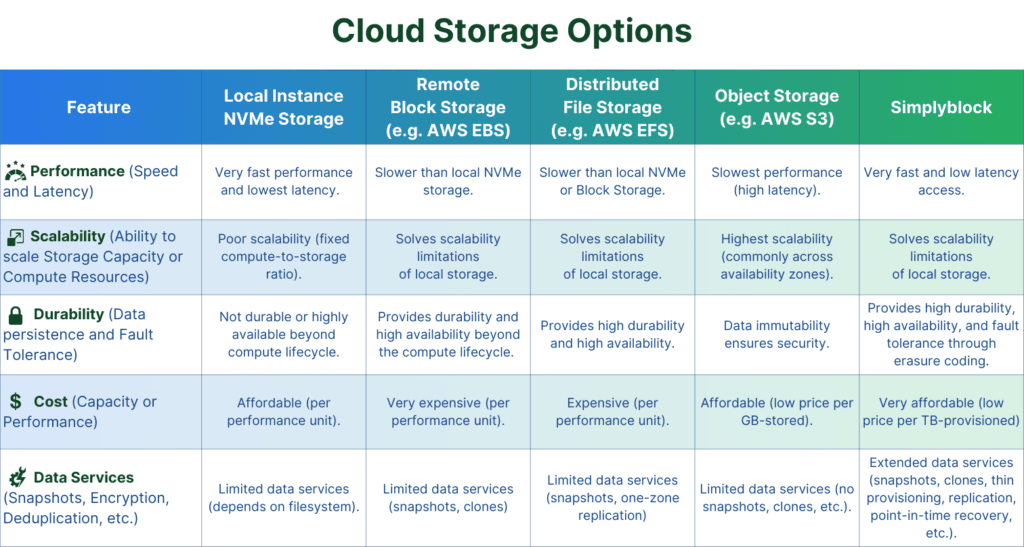
As cloud users, we have to choose between the following options:
- Local, fast NVMe storage has an affordable cost of performance and capacity but does not scale. A fixed ratio of compute to storage almost always leads to under- or over-utilization. They also do not live beyond the lifecycle of the single compute instance. It is, therefore, neither highly durable nor highly available. Further, it does not come with additional data services that are effective in increasing storage efficiency and decreasing storage costs or increasing security and reliability, such as thin provisioning, deduplication, compression, encryption, attack detection, snapshots, copy-on-write clones, and many more.
- Remote fast block storage overcomes some of the limitations of local storage but is slower and much more expensive on a per-performance unit. Also, depending on the specific type and costs, it is not highly durable, cannot be multi-attached, replicated across availability zones, or doesn’t have special cyber-security protection features.
- Distributed file storage is comfortable and supports multi-tenancy but is expensive (per capacity, per performance unit), not as fast as local or networked block storage, not replicated across zones, and does not provide a range of data services. Object storage is the cheapest type of storage. It is highly scalable and works across availability zones but requires a separate programmatic interface. Furthermore, it is immutable and really slow, with high access latency. A limited amount of data services is available. It does not allow for features such as instant snapshotting and copy-on-write clones.
Storage Virtualization and the Cloud Future
Moving to the cloud robbed us of the possibility of combining the wanted features, and we had to settle on what the cloud provider provides. At simplyblock, we strongly believe this is not how it should be. People should have the freedom of choice they’ve known with their SAN and NAS storage solutions. Our industry doesn’t need to step back but move forward.
That said, at Simplyblock, we take the fundamental ideas and concepts of storage virtualization and adapt them to achieve the next level of cloud computing. By optimizing cloud storage efficiency, Simplyblock enables organizations to reduce their cloud storage carbon footprint while maintaining performance. We seamlessly combine different cloud storage types into a single logical device, exposing the solution over the most common industry interface for fast storage—NVMe over TCP—compatible with all modern Linux and Windows servers.

With this approach, you can combine the cost efficiency and reliability of object storage with the convenience and performance of networked storage. You can even utilize the ultra-low latency of your local storage. All storage is transparently tiered and moved between the layers. A common set of data services, such as thin provisioning, instant snapshots, instant cloning, replication, cyber-security features, and deduplication, are available across all.
This way, we can make the best of the latest generation of high-end data center storage systems and architectures and make them available to you as needed. They are fully configurable.
The Future is now
At simplyblock, we already build the future. We believe the primary concern is the freedom to combine storage requirements according to your needs. Unfortunately, cloud providers have a different agenda. They try to build a solution that works for as many as possible. On the other side, they help the cloud provider’s financial business side.
Anyway, the technology is available and can be used today. There is no need to wait for tomorrow. The future is now.
If you want to learn more about how simplyblock works, you must read our “why simplyblock” page, and when you’re ready to try it out, let us know.
Questions and Answers
Storage virtualization in cloud computing abstracts physical storage across devices into a unified pool. This enables dynamic allocation and centralized management. It’s foundational for cloud storage cost optimization and efficient scaling in hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Storage virtualization enhances flexibility, increases storage utilization, and simplifies operations. By decoupling storage from hardware, it aligns well with software-defined storage strategies and supports modern data center architectures focused on agility and automation.
While both abstract physical storage, storage virtualization focuses on pooling resources, and software-defined storage (SDS) extends that by delivering policy-driven provisioning and automation through software. SDS leverages virtualization as a core component but adds orchestration layers.
Yes, by abstracting and optimizing storage across nodes, virtualization supports better IOPS and latency for Kubernetes workloads. When combined with fast protocols like NVMe over TCP, it provides high-performance persistent volumes for containerized apps.
It provides a scalable foundation for managing growing data volumes while ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. It also integrates with features like RPO and RTO reduction for disaster recovery planning and secure multi-tenant storage provisioning
